總共6題
- shop
- magic
- ret2libc
- doll
- fmt
- hello
shop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void purchase(int price, int your_money) {
int amount;
puts("Input the amount:");
scanf("%d", &amount);
if(amount > 0){
int total_price = price*amount;
if(your_money >= total_price){
your_money -= total_price;
printf("You have purchased the flag\n");
getFlag();
}
else {
puts("You don't have enough money!");
}
}
else{
puts("Invalid amount!");
}
}
void getFlag() {
puts(getenv("FLAG"));
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
int flag_price = 999999, your_money = 10, choice;
puts("Welcome to the server:");
while(1) {
printf("Current money: %d\n", your_money);
puts("1. Purchase Flag");
puts("2. Exit");
puts("Input your choice:");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch(choice) {
case 1:
purchase(flag_price, your_money);
break;
case 2:
exit(0);
default:
puts("Invalid choice!");
break;
}
}
}
|
可以看到main會呼叫purchase,然後purchase會比較輸入的數量 * 999999和10,只要運用integer overflow讓數量 * 999999爆開就可以拿到flag了
magic
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
char secret[0x10];
void init()
{
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stderr, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < 0x10; i++)
{
secret[i] = 48 + (rand() % (126 - 47) + 1);
}
}
int main(){
init();
puts("Please enter the secret: ");
char input[0x10];
read(0, input, 0x10);
if (strcmp(input, secret) == 0)
{
puts("You got it! Here is your flag!");
puts(getenv("FLAG"));
}
else
{
puts("Guess wrong!");
}
return 0;
}
|
這邊可以看到secret是用srand(time(0))產生的,可以用python裡的ctype來設srand的seed,把它設成time.time()然後用一樣的方法產生secret再送過去就可以拿到flag了
ret2libc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void hackMe() {
char buf[128];
read(0, buf, 256);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
puts("Welcome to the server!");
hackMe();
puts("Goodbye!");
}
|
這題的flag存在機器上的flag.txt,要rce才行。
我有裝gdb peda,checksec看一下
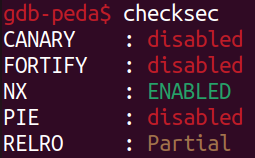
只有開NX,我選擇用ret2libc來做。
一開始的思路是直接送到overflow之後,用plt puts出puts的got,洩漏出libc的base address,然後再用system(“/bin/sh”)來拿flag,但是這個小小的程式裡面找不到pop rdi的gadget,這條路沒辦法拿到libc base
後來我看了看main裡面,發現stdin和stdout的真實地址是存在0x404050裡面,這個地址是got table的範圍,裡面存的address是在libc裡面的。
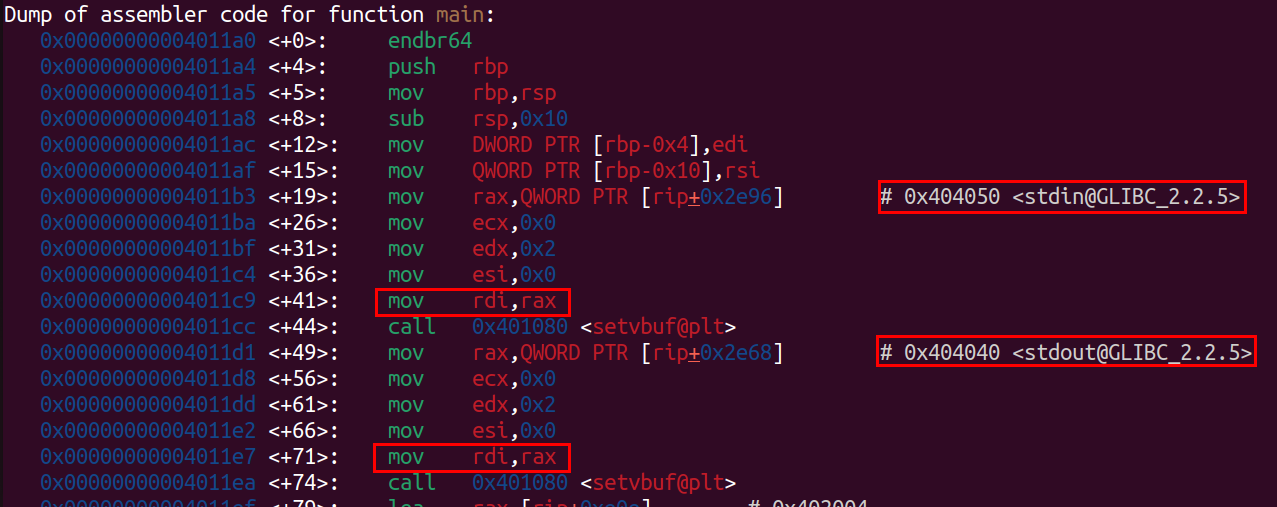

目前想到用got table hijacking,把setvbuf變成puts。
用 objdump -R 看一下got table有什麼
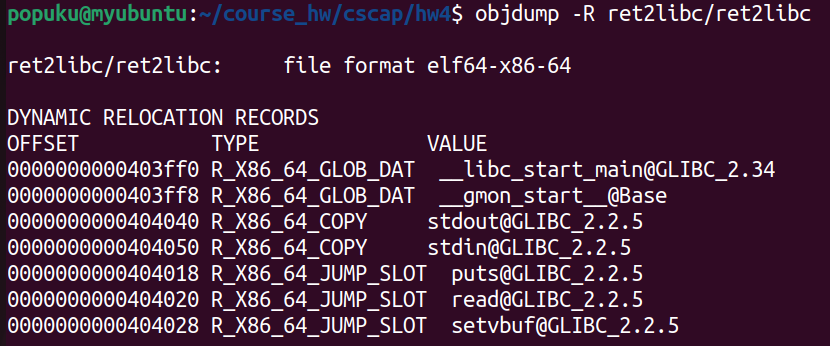
GOT table範圍
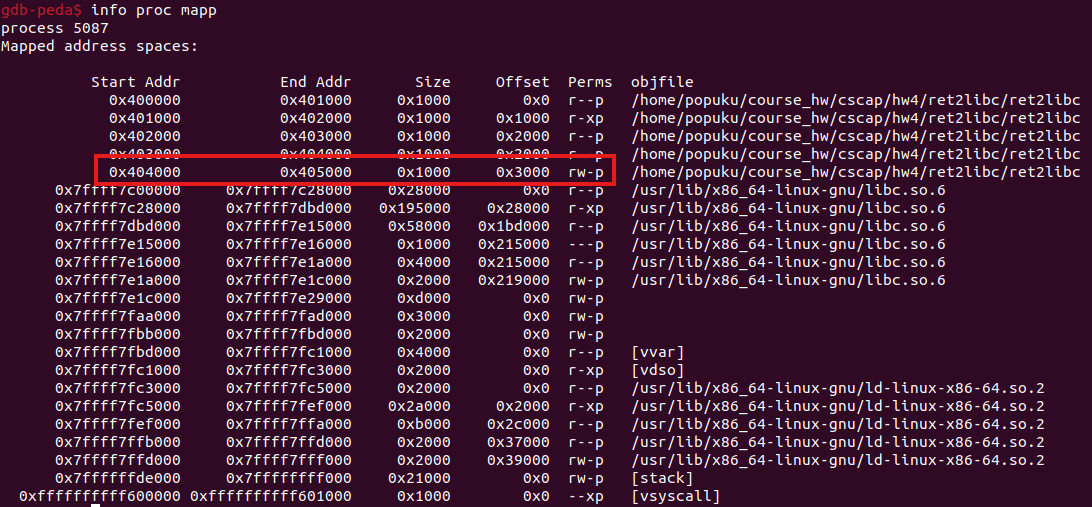
因為GOT table裡面是可以寫的,我們可能可以把setvbuf的got改成puts@plt的位置,然後把stdin改成0x404040,等於puts的參數是指向0x7ffff7e1b780的一個pointer,這樣在跳回main執行setvbuf(stdin, …)的時候,就等同於執行puts(*(0x7ffff7e1b780)),我們就可以得到這個值減掉offset拿到libc base了。
現在的重點是要怎麼覆寫setvbuf的got,目前唯一可以讓我們任意寫的地方就只有read了。
我在這個 raddit的貼文 看到有人用overflow把stack上的rbp變成got附近的位置,leave的時後相當於mov rsp, rbp; pop rbp,所以就可以控制rbp的值;之後再執行到read的時候,輸入的東西就會寫到rpb - 0x80的位置,只要把rpb蓋成setvbuf在got table的地址 + 0x80,就可以把puts的地址寫到setvbuf的got table裡面了。
用read把puts的plt寫到setvbuf的got table裡面的時候要注意,只要程式一執行read,在ret之前一定就會leave,要蓋掉rpb + buffer size的話整個stack都會跑到got table附近,我們需要自己把stack盡可能的塞到可寫的區域裡面,然後好好控制rbp和rsp的位置。
現在要注意的一點就是setvbuf因為在比stdin和stdout都低的位置,而因為puts的時候會檢查stdout有沒有壞掉,所以要想一下要怎麼蓋掉setvbuf和stdin,而且之後可以ret到main裡面執行setvbuf。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| GOT table:
0x405000 xxx <- 可寫的最高位置
... <- rpb和rsp會在這
0x404058 ...
0x404050 | stdin | <- 要蓋成0x404040 (相當於指向stdout的地址的pointer,puts才洩漏得出來)
0x404048 | |
0x404040 | stdout | <- 不可以蓋掉
...
0x404028 | setvbuf | <- 蓋成puts@plt (0x404018)
0x404020 | read |
0x404018 | puts |
...
0x404000 xxx <- 可寫的最低位置
|
我的方法就是要先在setvbuf + 0x80附近先設好在覆蓋完setvbuf之後rbp,ret的地址,順便把stdin蓋成0x404040;rbp需要到更高的地方加大stack的大小 (0x405000附近),ret會是main+19的地方,之後還會有一次機會可以read,去讓程式執行system(‘bin/sh’)。
exp: ret2libc.py
doll
這題算是misc,給了一張圖。
Matryoshka dolls.jpg
用hex editor打開,查了一下jpg結尾的EOI bytes(0xFFD9),發現他在offset 0x6ADC的位置,然後那附近又看到PNG的bytes,推測可能是又有一張png圖在檔案的尾部。
用dd把它切出來,然後用hex editor打開,發現正好就是一個有flag的png。
1
| dd if="$filename" of=flag.png bs=1 skip=27424
|
flag.png
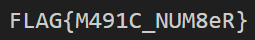
fmt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
char flag[40] = "FLAG{??????????????????????????????????}";
char input[24];
scanf("%s", input);
printf(input);
return 0;
}
|
這邊是要我們好好用format string的弱點來洩漏flag。
用gdb找一找應該就可以看出來offset在哪了。
exp: fmt.py
hello
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char name[0x20] = "user";
void init(){
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stderr, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
}
int read_int(){
char buf[0x10];
read(0, buf, 0x10);
return atoi(buf);
}
void hello() {
puts("Hello, Hello, Hello~~~");
}
void editName(){
char input[0x20];
char y = '\0';
while (1){
puts("Enter your new name");
write(1, "> ", 2);
read(0, input, 0x80);
printf("Set fans name to %s (Y/N)\n", input);
y = getchar();
if (y == 'Y' || y == 'y'){
break;
}
}
strcpy(name, input);
puts("Name changed!");
}
int main(){
init();
puts("Welcome to the hello server, try to get the flag!\n");
int choice = 0;
while (1){
puts("1. Edit Name");
puts("2. Say Hello");
puts("3. Exit");
puts("Input your choice:");
choice = read_int();
switch (choice){
case 1:
editName();
break;
case 2:
hello();
break;
case 3:
exit(0);
break;
default:
puts("Invalid argument!!");
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
|
在editName那邊有一個迴圈可以輸入到input,他是用read(0, input, 0x80),而input只有開0x20。
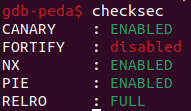
看一下checksec,發現有開PIE,CANARY和NX,可能需要leak出ret address、canary和libc base,然後再用ret2libc來做。
首先gdb看一下,需要傳0x28 + 1個bytes才能leak出canary。
然後要執行system需要libc base,這支程式也沒有pop rdi; ret的gadget,所以要看一下程式執行到read的時候附近的記憶體有沒有在libc範圍內的地址,讓它在printf的時候洩漏出來。
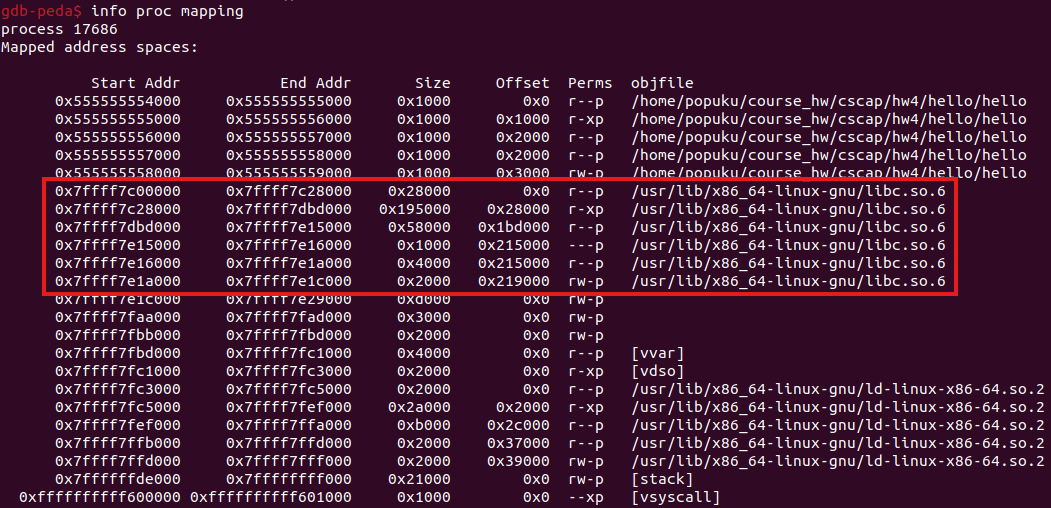
可以看到libc的範圍在0x7ffff7c00000 ~ 0x7ffff7e1c000。
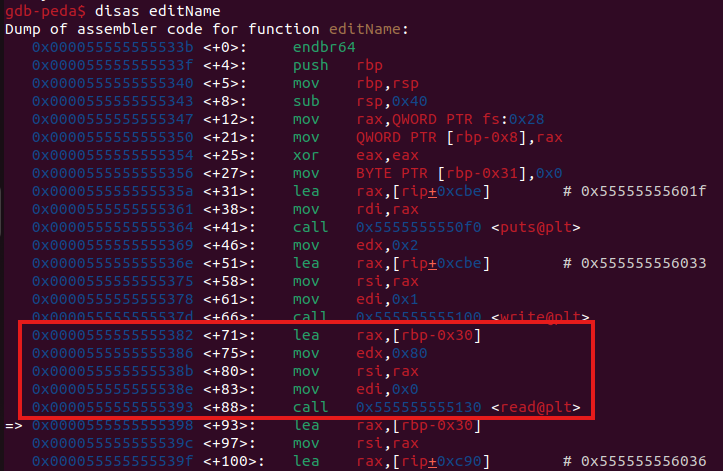
editName read的input會從rbp - 0x30的地方開始寫,我們就去看一下rbp - 0x30的地方有沒有在libc範圍內的地址。
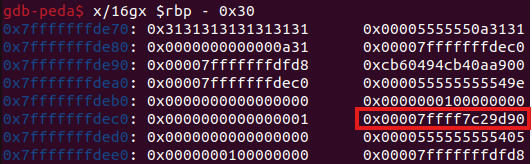
我設了一個斷點到read的地方,然後輸入1111111111,在去看記憶體從rbp - 0x30開始往高記憶體有沒有在libc範圍內的地址,結果還真的有,就是這張圖裡面框起來的地方。
拿這個值減掉0x7ffff7c00000就可以拿到這個地方的offset是0x29d90,之後可以用read來leak出每次process跑起來的libc base了。
有了這些就可以拿libc裡面的pop rdi; ret gadget來做ret2libc了。
exp: hello.py









